NVIDIA has utilized its GPU architecture to create platforms for scientific computing, artificial intelligence (AI), data science, autonomous vehicles, robotics, and augmented and virtual reality. Co. has two segments: Graphics, which includes GeForce GPUs for gaming and PCs, the GeForce NOW game streaming service and related infrastructure, and solutions for gaming platforms, and Quadro/NVIDIA RTX GPUs for enterprise workstation graphics; and Compute and Networking, which includes Data Center platforms and systems for AI, high-performance computing, and accelerated computing, Mellanox networking and interconnect solutions, and cryptocurrency mining processors.
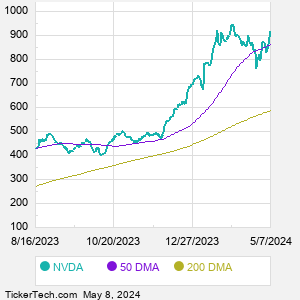
When researching a stock like NVIDIA, many investors are the most familiar with Fundamental Analysis — looking at a company's balance sheet, earnings, revenues, and what's happening in that company's underlying business. Investors who use Fundamental Analysis to identify good stocks to buy or sell can also benefit from NVDA Technical Analysis to help find a good entry or exit point. Technical Analysis is blind to the fundamentals and looks only at the trading data for NVDA stock — the real life supply and demand for the stock over time — and examines that data in different ways. One of these ways is called the Relative Strength Index, or RSI. This popular indicator, originally developed in the 1970's by J. Welles Wilder, looks at a 14-day moving average of a stock's gains on its up days, versus its losses on its down days. The resulting NVDA RSI is a value that measures momentum, oscillating between "oversold" and "overbought" on a scale of zero to 100. A reading below 30 is viewed to be oversold, which a bullish investor could look to as a sign that the selling is in the process of exhausting itself, and look for entry point opportunities. A reading above 70 is viewed to be overbought, which could indicate that a rally in progress is starting to get crowded with buyers. If the rally has been a long one, that could be a sign that a pullback is overdue. |